1. Introduction
What is a computer?
2. Listening comprehension.
|
Watch this video once. |
3. Reading comprehension.
A computer is an electronic device that manipulates information, or data. It has the ability to store, retrieve, and process data. You may already know that you can use a computer to type documents, send email, play games, and browse the Web. You can also use it to edit or create spreadsheets, presentations, and even videos.
3.1. Hardware vs. software.
Before we talk about different types of computers, let’s talk about two things all computers have in common: hardware and software.
-
Hardware is any part of your computer that has a physical structure, such as the keyboard or mouse. It also includes all of the computer’s internal parts.
-
Software is any set of instructions that tells the hardware what to do and how to do it. Examples of software include web browsers, games, and word processors.
Everything you do on your computer will rely on both hardware and software. For example, right now you may be viewing this lesson in a web browser (software) and using your mouse (hardware) to click from page to page. As you learn about different types of computers, ask yourself about the differences in their hardware. As you progress through this tutorial, you’ll see that different types of computers also often use different types of software.
3.2. What are the different types of computers?
When most people hear the word computer, they think of a personal computer such as a desktop or laptop. However, computers come in many shapes and sizes, and they perform many different functions in our daily lives. When you withdraw cash , scan groceries at the store, or use a calculator, you’re using a type of computer.
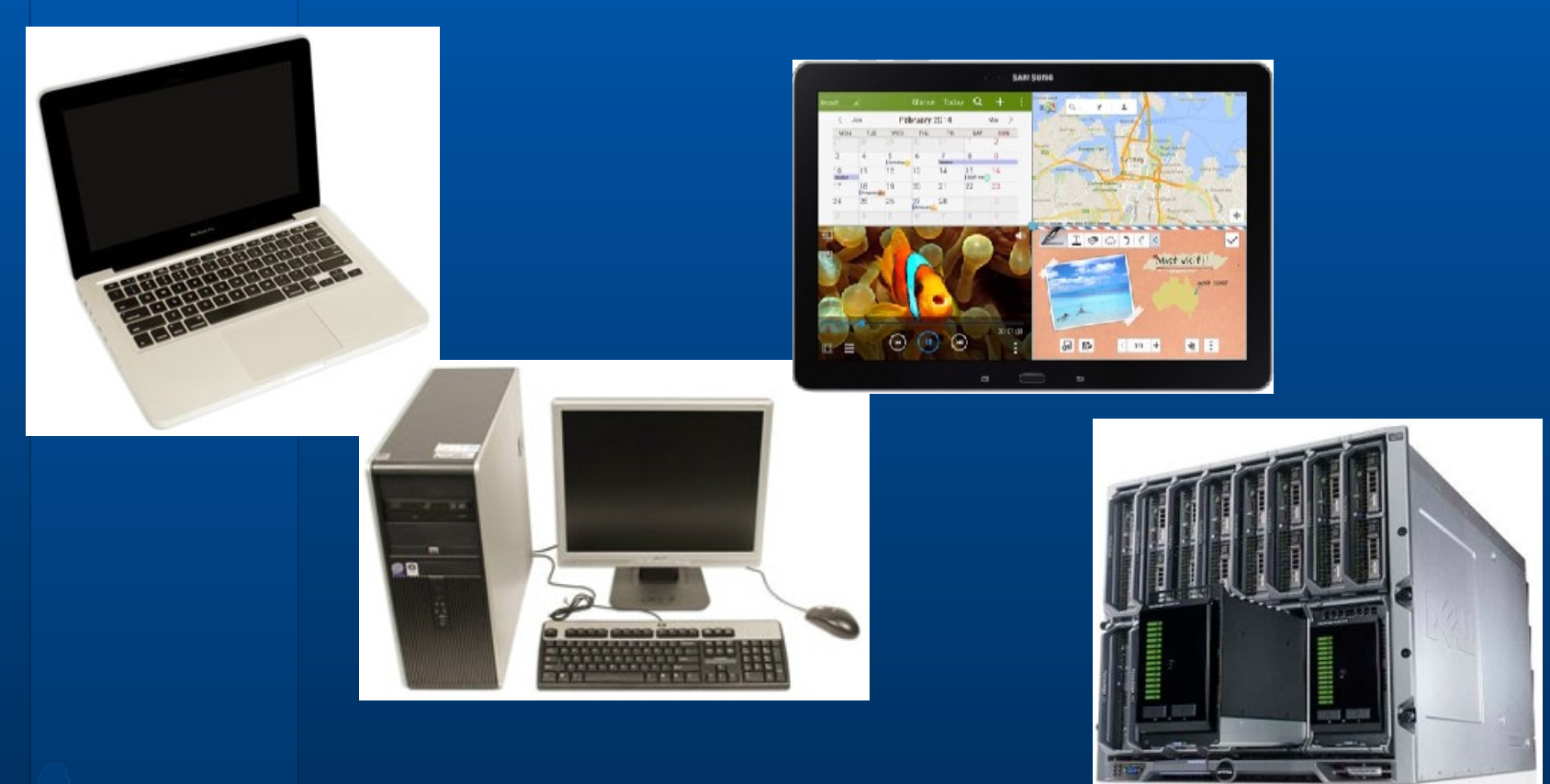

3.2.1. Desktop computers.
Many people use desktop computers at work, home, and school. Desktop computers are designed to be placed on a desk, and they’re typically made up of a few different parts, including the computer case, monitor, keyboard, and mouse.
3.2.2. Laptop computers.
The second type of computer you may be familiar with is a laptop computer, commonly called a laptop. Laptops are battery-powered computers that are more portable than desktops, allowing you to use them almost anywhere.
3.2.3. Tablet computers.
Tablet computers—or tablets—are handheld computers that are even more portable than laptops. Instead of a keyboard and mouse, tablets use a touch-sensitive screen for typing and navigation. The iPad is an example of a tablet.
3.2.4. Servers.
A server is a computer that serves up information to other computers on a network. For example, whenever you use the Internet, you’re looking at something that’s stored on a server. Many businesses also use local file servers to store and share files internally.
3.2.5. Other types of computers.
Many of today’s electronics are basically specialized computers, though we don’t always think of them that way. Here are a few common examples.
-
Smartphones: Many cell phones can do a lot of things computers can do, including browsing the Internet and playing games. They are often called smartphones.
-
Wearables: Wearable technology is a general term for a group of devices—including fitness trackers and smartwatches—that are designed to be worn throughout the day. These devices are often called wearables for short.
-
Game consoles: A game console is a specialized type of computer that is used for playing video games on your TV.
-
TVs: Many TVs now include applications—or apps—that let you access various types of online content. For example, you can stream video from the Internet directly onto your TV.
3.3. PCs and Macs
Personal computers come in two main styles: PC and Mac. Both are fully functional, but they have a different look and feel, and many people prefer one or the other.
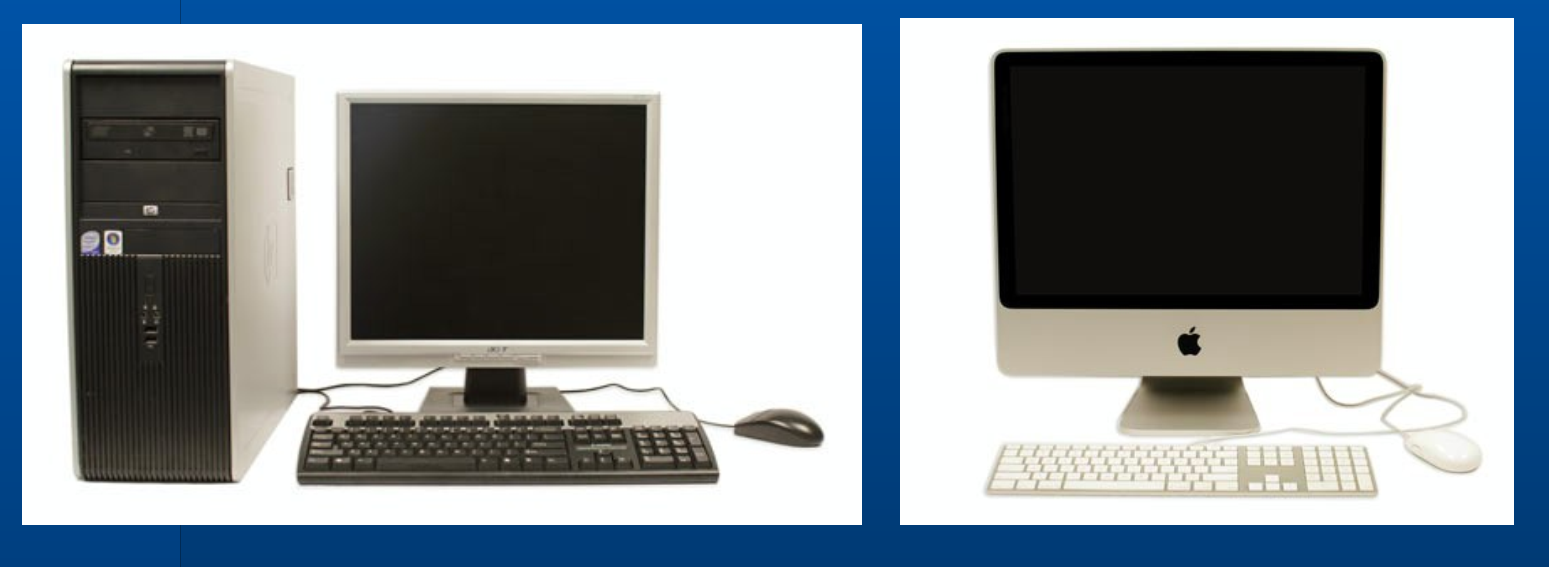

3.3.1. PCs
This type of computer began with the original IBM PC that was introduced in 1981. Other companies began creating similar computers, which were called IBM PC Compatible (often shortened to PC). Today, this is the most common type of personal computer, and it typically includes the Microsoft Windows operating system.
3.3.2. Macs
The Macintosh computer was introduced in 1984, and it was the first widely sold personal computer with a graphical user interface, or GUI. All Macs are made by one company (Apple), and they almost always use the Mac OS X operating system.
4. Let’s play


|
Watch this video again. |
5. Writing comprehension.
Now, you can fill out this document.
6. already finished!
Watch these videos on computer sciences:
7. Basic Parts of a Computer
The basic parts of a desktop computer are the computer case, monitor, keyboard, mouse, and power cord. Each part plays an important role whenever you use a computer.
|
Watch this video once. |
7.1. Computer case

The computer case is the metal and plastic box that contains the main components of the computer, including the motherboard, central processing unit (CPU), and power supply. The front of the case usually has an On/Off button and one or more optical drives. Computer cases come in different shapes and sizes. A desktop case lies flat on a desk, and the monitor usually sits on top of it. A tower case is tall and sits next to the monitor or on the floor. All-in-one computers come with the internal components built into the monitor, which eliminates the need for a separate case.
7.2. Monitor

The monitor works with a video card, located inside the computer case, to display images and text on the screen. Most monitors have control buttons that allow you to change your monitor’s display settings, and some monitors also have built-in speakers. Newer monitors usually have LCD (liquid crystal display) or LED (light-emitting diode) displays. These can be made very thin, and they are often called flat-panel displays. Older monitors use CRT (cathode ray tube) displays. CRT monitors are much larger and heavier, and they take up more desk space.
7.3. Keyboard.

The keyboard is one of the main ways to communicate with a computer. There are many different types of keyboards, but most are very similar and allow you to accomplish the same basic tasks.
7.4. Mouse.
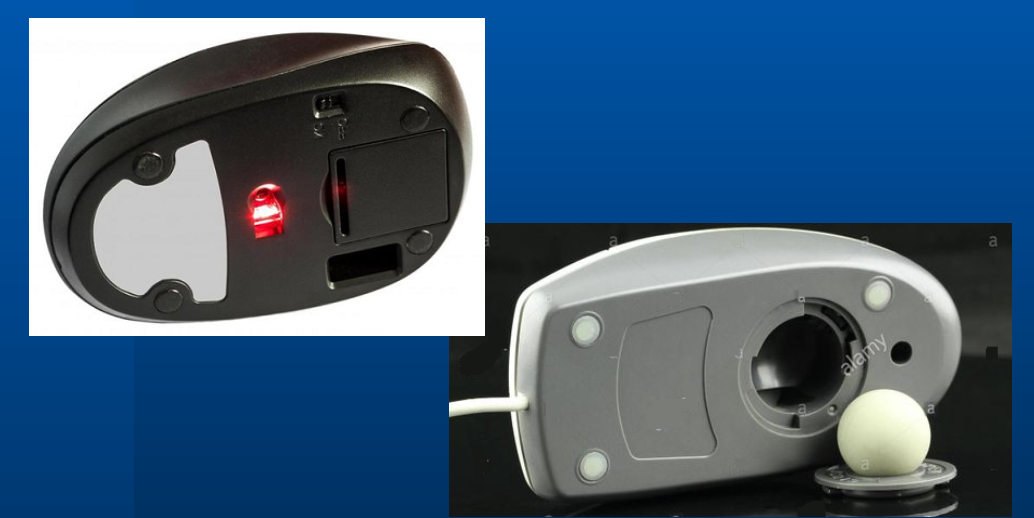

The mouse is another important tool for communicating with computers. Commonly known as a pointing device, it lets you point to objects on the screen, click on them, and move them. There are two main mouse types: optical and mechanical. The optical mouse uses an electronic eye to detect movement and is easier to clean. The mechanical mouse uses a rolling ball to detect movement and requires regular cleaning to work properly.
7.5. Mouse alternatives.

There are other devices that can do the same thing as a mouse. Many people find them easier to use, and they also require less desk space than a traditional mouse. The most common mouse alternatives are below.
-
Trackball: A trackball has a ball that can rotate freely. Instead of moving the device like a mouse, you can roll the ball with your thumb to move the pointer.
-
Touchpad: A touchpad—also called a trackpad—is a touch-sensitive pad that lets you control the pointer by making a drawing motion with your finger. Touchpads are common on laptop computers.
8. Let’s practice.
9. Writing comprehension.
Now, you can fill out this document.
